What is Transmittance?
Transmittance usually refers to the proportion of light that is not reflected or absorbed when passing through a material . It is usually expressed as a percentage (%) . For example, within a certain wavelength range, if 100% of the light is projected onto a material and 80% of the light passes through the material, the transmittance is 80%. Transmittance is one of the important indicators in optical measurement, especially in evaluating the transparency, clarity and optical properties of materials. Transmittance measurement is widely used in scientific research, material manufacturing and product quality control.
The difference between Transmittance and Transparency
Transmittance and transparency are often confused, but they actually have different meanings. Transmittance is a quantitative indicator that represents the proportion of light that passes through a material. Transparency is more of a sensory measurement , reflecting the "clearness" of an object. The level of transmittance can objectively evaluate transparency, but transparency is also affected by other factors such as haze and color. Therefore, materials with high transmittance do not always appear visually transparent . For example, frosted glass has a certain level of transmittance but a high haze, so the transparency is not high .
Relationship between Transmittance and Haze
Haze indicates the degree of scattering of light after passing through a material. Transmittance and haze are two key parameters that affect the transparency and optical properties of a material. The main differences between transmittance and haze are as follows:
1. Transmittance indicates the proportion of light that passes through a material , with higher values representing more light passing through .
2. Haze reflects the degree of scattering of transmitted light. The lower the value, the less scattered the light and the clearer the image. The higher the value, the blurrier it is.
A material can have high transmittance but also high haze value, such as frosted glass; although light can pass through, the image is blurry. The relationship between the two plays an important role in the application scenarios of materials. Reasonable regulation of transmittance and haze can significantly optimize the optical properties of materials to meet different industrial needs.
How to measure Transmittance? Transmittance measurement method
The transmittance can be measured using a 3nh transmittance meter/haze meter and a desktop spectrophotometer. The following are the two transmittance measurement methods.
1. Spectrophotometer method: A beam of light is irradiated onto the sample to be tested, and the transmittance is calculated by measuring the light intensity before and after the light passes through the sample. The measurement results can usually be accurate to a specific wavelength range, thus obtaining the transmittance of the material at different wavelengths.
2. Transmittance meter: This instrument is designed to measure the light transmittance of materials. Through simple operation, the transmittance value can be directly obtained. It is suitable for production lines and quality inspections. The transmittance meter can detect the transmittance of materials to different types of light. Common wavebands include 850nm and 950nm infrared transmittance, 365nm ultraviolet transmittance, 550nm visible light transmittance, and 380-760nm white light visible light transmittance.
Transmittance measurement standards
Different industries and materials have different transmittance measurement standards, including:
· ASTM D1003 : Standard Test Method for Haze and Luminous Transmittance of Transparent and Translucent Plastics.
· ASTM D1044 : Mainly used to evaluate the wear resistance and scratch resistance of materials to ensure the optical quality of materials in long-term use.
· ISO 13468 : Mainly used for light transmittance testing of plastic materials, it specifies the measurement methods of optical properties in transmission and scattering modes.
· ISO 9050 : Standard method for light transmittance and energy transmission of glass materials, commonly used in areas such as architectural and automotive glazing.
Compensated and non-compensated Transmittance measurements
Luminous transmittance: The ratio of the luminous flux passing through the sample to the luminous flux hitting the sample, expressed as a percentage.
According to the above definition of luminous transmittance, there are currently two different standards to measure this data. They are the American standard (ASTM standard) and the international standard (lSO standard).These two respective standards correspond to the non-compensation method of transmittance measurement and the compensation method of transmittance measurement.
1. Non-compensation method for measuring transmittance :
Non-compensation measurement method When the standard reflectance plate is placed at the light exit port of the light path, the measurement is performed when the sample is removed.
The data read by the photoelectric sensor is T1, which is the total energy of the incoming light. Place the sample in the transmission port for measurement. The data read by the photoelectric sensor is T2, which is the total energy of the incident light absorbed by the sample. Then the calculation formula for transmittance can be obtained:
T=T2/T1
The above is the transmittance of the sample, and this method is the transmittance measured by the non-co- empensation method.
2. Transmittance compensation measurement method
In the above non-compensation measurement method, if we study carefully, we will find that when we measure T2, the value of T2 is not only the total energy of the incident light absorbed by the sample, but also includes the reflected energy of the sample surface after the integrating sphere is illuminated to the sample surface, and we did not consider the reflected energy of the sample surface when measuring T1. This is a certain deviation that occurs when the non-compensation method measures light transmittance. Therefore, the International Organization for Standardization (lSO) proposed a method for measuring transmittance based on compensation.
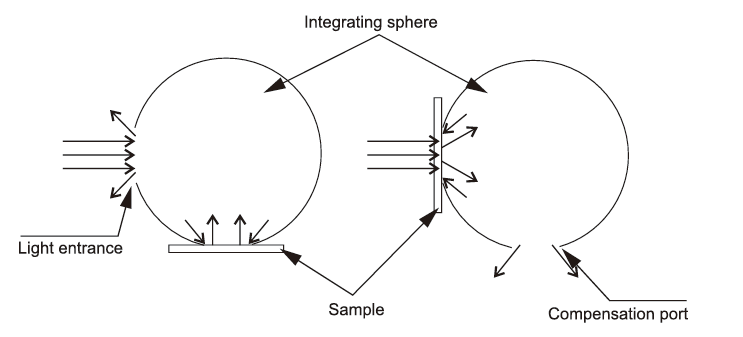
Figure 60 Schematic diagram of measurement principle of compensation method
The measurement method of the compensation port is as follows. First, place the sample surface on the compensation port and measure the total energy T1 of the incident light. At this time, the T1 value already includes the reflected energy value of the illuminated integrating sphere irradiated on the sample surface, and then place the sample at the transmission port and measure the total energy value T2 of the incident light after passing through the sample. The T2 value at this time also includes the reflected energy value of the illuminated integrating sphere irradiated on the surface of the sample. Then the calculation formula of transmittance can be obtained:
T=T2/T1
The transmittance value at this time takes into account the reflection of the sample surface and is more accurate. This method is the transmittance measured by the compensation method. Based on the above-mentioned test principle and formula derivation and comparison of actual test data, the transmittance measured by the non-compensation method is slightly different from the transmittance measured by the compensation method, but the difference is not large. The transmittance measured by the compensation method is more accurate.
Application of Transmittance
Transmittance has a wide range of applications in many fields. The following are some of the main application scenarios:
1. Optical industry
· Glasses and lens manufacturing : Transmittance is an important indicator to measure the light transmission performance of products such as eyeglass lenses, sunglasses, and contact lenses. A higher transmittance ensures a clear field of vision, while sunglass lenses usually need to control transmittance to reduce the impact of strong light on the eyes.
· Optical filters : In optical instruments, filters pass specific wavelengths of light and block other wavelengths. Precise control of transmittance can achieve specific optical effects such as color adjustment and spectral analysis.
2. Architectural and automotive glass
· Windows and thermal insulation glass : The transmittance of building and automotive glass directly affects the lighting and thermal insulation performance. Appropriate transmittance can ensure sufficient indoor lighting while reducing the transmission of ultraviolet and infrared rays to reduce energy consumption and protect personal safety.
· Safety and privacy glass : Some special glasses, such as one-way perspective glass and frosted glass, achieve privacy protection by controlling transmittance while maintaining visual transparency in appropriate scenarios.
3. Agriculture
· Greenhouse and agricultural films : The transmittance of greenhouse films directly affects the photosynthesis and growth of crops. By adjusting the transmittance of the film, it is possible to ensure the right amount of sunlight enters while controlling temperature and humidity.
· Agricultural lighting : Transparent materials with specific wavelengths can be used for plant lighting, helping plants obtain optimal lighting conditions in the greenhouse and promoting growth.
3nh Transmittance measurement solution
1. 3nh Benchtop Spectrophotometer
3nh YS6002 instrument is equipped with a 360~780nm full-spectrum high-lifetime light source, an optical system with an optical resolution of 10nm, and built-in multiple color spaces and color difference formulas , which can express the chromaticity of samples in multiple dimensions. The instrument also accurately measures the haze and transparency of transmission samples in accordance with ASTM D1003/D1044 standards .
2. 3nh Color Haze Meter
3nh YH1810 is designed according to CIE transmission geometry optical structure transmission 0/D (parallel light illumination, diffuse reflection reception). The instrument can easily implement ASTM D1003 non-compensation method, ISO 13468 compensation method, full transmittance, haze test, clarity measurement, and color data comparison. It can accurately collect the transmittance spectrum curve of the transmission sample and accurately output various color data of the transmission sample.









 0086 18165740359
0086 18165740359 Skype Online
Skype Online