In color measurement, SCI (Specular Component Included) and SCE (Specular Component Excluded) are two measurement modes. The main difference between them is whether the surface specular reflection component is included . SCI and SCE generally only appear in the setting options of the colorimetric instrument of the d/8 structure integrating sphere . Now most of the d/8 integrating sphere structure measurement equipment support both SCI and SCE measurement modes, such as 3nh TS70 series spectrophotometer, which supports both SCI and SCE measurement modes . Different measurement modes will lead to differences in color data, so it is very important to understand the definition and use of SCI and SCE.
What is SCI?
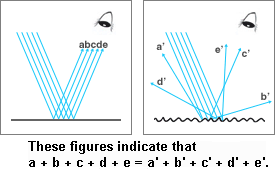
SCI (Specular Component Included) refers to a measurement mode that includes specular reflection . In SCI mode, the color measurement instrument captures all reflected light, including specular reflection and diffuse reflection. Specular reflection refers to the strong light reflected from the smooth area of the object surface, which is closely related to the observation angle.
· Features : SCI mode can effectively reduce the influence of factors such as surface texture, gloss, scratches, etc., so as to more accurately reflect the color itself.
· Applicable scenarios : Usually used in laboratories and quality control, especially when comparing the colors of different samples to ensure comparability between samples.
· Advantages : SCI can obtain more consistent color data, which is suitable for scenes that require precision and good repeatability, especially for materials with uneven surfaces.
What is SCE?
SCE (Specular Component Excluded) refers to the measurement mode that excludes specular reflection components . In SCE mode, the instrument excludes specular reflection light from the measurement results by adjusting the angle or adding optical devices, and only retains diffuse reflection light components. Diffuse reflection light refers to non-directional reflection light generated by rough surface areas.
· Features : The measurement results of SCE mode are closer to the observation results of human eyes because it avoids the influence of bright light spots on color judgment.
· Applicable scenarios : Suitable for measuring objects with obvious surface gloss and texture. Especially when simulating the human eye's color perception of objects, the SCE mode is more in line with the visual experience.
· Advantages : Closer to actual appearance, suitable for final quality assessment of products, such as color measurement of textiles, leather, coatings, etc.
What is the difference between SCI and SCE?
The main difference between SCI and SCE is the way the specular component is handled . Specifically:
|
Measurement Mode |
definition |
Applicable scenarios |
advantage |
shortcoming |
|
SCI |
Contains specular component |
Quality control, laboratory measurements |
High measurement stability, not affected by surface gloss |
Does not conform to the actual perception of the human eye |
|
SCE |
Excluding specular reflections |
Visual color detection, materials with obvious texture |
The result is closer to human eye perception |
Data stability is low and affected by surface gloss |
· Accuracy : The color data measured by the SCI mode will be more consistent, reducing the influence of surface texture and gloss, and is suitable for accurate comparison under laboratory conditions. The SCE mode excludes specular reflection components and is closer to the visual perception of the human eye, making it suitable for visual color evaluation.
· Result consistency : SCI mode has higher measurement consistency, while SCE mode is more susceptible to changes in surface gloss and the results may fluctuate slightly.
· Measurement target : SCI mode focuses on the "real color" of the object and is suitable for comparing the color consistency of the same product batch. SCE is more suitable for perceiving the "surface appearance" of the object and is suitable for final appearance inspection.
When measuring color, should I choose SCI or SCE?
The choice of SCI or SCE depends on the measurement objectives and application scenarios:
1. stable and accurate color data is required , such as quality control under laboratory conditions and raw material comparison, it is recommended to choose SCI mode. SCI mode can ensure the consistency of color data between samples, eliminate the influence of surface reflection, and is more suitable for professional comparative analysis. Plastics, coatings, automotive industries and other industries with high requirements for surface consistency are more suitable for SCI mode to ensure the consistency of material color.
2. Simulating human eye perception : For the appearance inspection of the final product (especially for products that have a greater impact on the perception of end consumers), it is recommended to use the SCE mode. The SCE mode can better show the actual color seen by the human eye, especially for objects with strong texture and high gloss.
In addition, although the color of the material itself does not change, the amount of specular and diffuse reflection on its surface will change due to different surface smoothness, which in turn affects the visual effect. For example, after polishing the surface, the specular reflection decreases and the diffuse reflection increases, making the surface look more matte. Therefore, measuring the total reflectance (specular reflection + diffuse reflection) helps to more accurately understand the surface characteristics and color stability of the material. The 3nh spectrophotometer can measure SCE+SCI at the same time to meet your different measurement needs.








 0086 18165740359
0086 18165740359 Skype Online
Skype Online