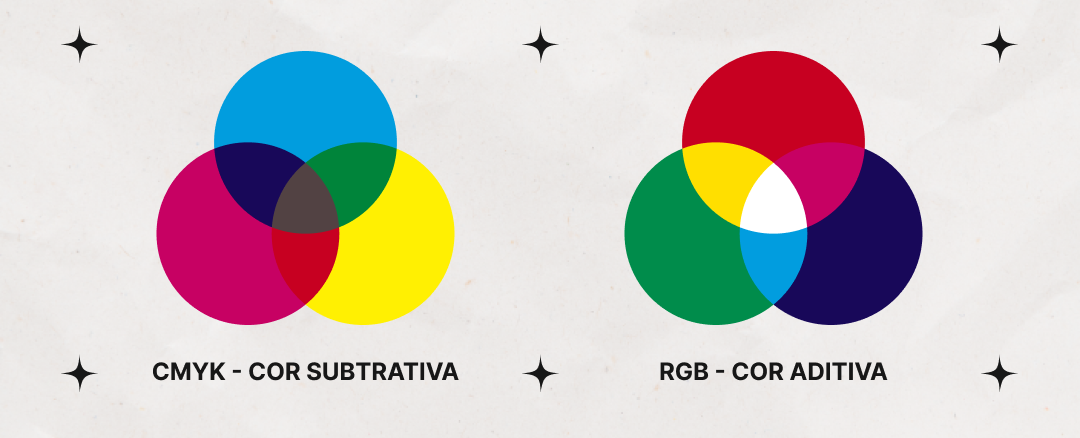
The CMYK color space is a subtractive color model used for printing. It presents various colors based on the combination of four color inks: cyan, magenta, yellow, and black (Key, K).

The CMYK color space is widely used in the printing industry and is suitable for expressing the color effects required in physical printing. The following is a detailed introduction to the CMYK color space:
1. The basic principle of CMYK
Subtractive color model: CMYK color space is a representative of the subtractive color model. Its principle is to use the absorption and reflection of light by ink. The more ink and the thicker it is, the less light is reflected. Therefore, by superimposing different proportions of cyan, magenta and yellow ink, various colors can be produced.
Four-color overlay: In actual printing, using cyan, magenta, and yellow to produce black will result in deviation and increase the amount of ink. Therefore, black ink (K) is introduced, which not only can produce a darker black, but also helps to reduce ink consumption and improve the contrast and details of the printing effect.
2. CMYK color generation principle
In the CMYK color model, various colors are produced by combining four basic inks in different concentrations. For example:
-
Cyan + Yellow = Green
-
Cyan + Magenta = Blue
-
Magenta + Yellow = Orange
Different colors are achieved by adjusting the concentration and proportion of the four inks C, M, Y, and K. For example, reducing the proportion of cyan and magenta can make the color more yellow, while increasing the proportion of black can make the color darker.

3. The importance of black (K) in CMYK
Black separation: In the printing process, black is not only used to present black areas, but also to enhance dark details and contrast. This method is called black separation, which means reducing the reliance on black when mixing CMY, and using black ink alone to present dark areas.
Gray balance: The introduction of black helps achieve gray balance, ensuring that the neutral tones of the image are not cast, especially when delicate shadows and transition areas need to be displayed.
4. CMYK spot colors
Spot color means that when printing, the color is not synthesized by printing the four colors of CMYK, but is printed with a specific ink.
Similar to placing black ink alone, spot color ink refers to a pre-mixed specific color ink (or special pre-mixed ink) used to replace or supplement printing color (CMYK) ink, such as bright orange, green, fluorescent color, metallic gold and silver ink, etc., or it can be a hot stamping version, embossed version, etc., and can also be used as a local varnish version, etc. It is not mixed by the four colors of CMYK. Each spot color requires a dedicated printing plate when printing (which can be simply understood as a pair of spot color films, and a separate plate for the spot color when printing). Spot color means accurate color.
5. Differences between CMYK and RGB
Additive and subtractive colors: RGB (red, green, and blue) is an additive color model, suitable for self-luminous devices such as monitors and televisions; while CMYK is a subtractive color model, used for light-absorbing printed materials.
Different color gamut: RGB has a wider color gamut than CMYK, so many colors displayed on the screen cannot be fully represented by CMYK. This is why when designing printed works, color conversion between RGB and CMYK is often required.
6. Dot technology and halftone
In printing, each color of CMYK is realized by dot size and density. This technology is called halftone, and by adjusting the density and arrangement of dots, different colors and gradient effects can be formed visually.
Since CMYK uses physical ink to overlay colors, dots at different angles are usually used to avoid "moire", which is an interfering pattern that appears during printing.
7. Application scenarios of CMYK
Graphic printing: CMYK is widely used in the production of paper printed materials such as newspapers, magazines, advertisements, and books.
Package printing: In package design, CMYK is also used to print packaging boxes, labels, etc. made of various materials.
Large format printing: Large printed materials including billboards, banners, etc. also use CMYK color space to achieve the desired effect.
8. Color conversion and calibration
When designing, the conversion from RGB to CMYK may cause color distortion, so color calibration is required before final output. In professional printing processes, tools such as densitometers or spectrophotometers are usually used to check and adjust printed colors to ensure that they are consistent with the colors of the design.
Summarize
CMYK color space is an important tool in the printing field. It can reproduce rich color effects through the combination of cyan, magenta, yellow and black inks. Its principle is based on subtractive color mixing and relies on dot technology to achieve different shades and gradient effects of color. Different from the additive color mode of RGB, CMYK color space is more suitable for actual printing scenes to ensure color reproduction and consistency.








 0086 18165740359
0086 18165740359 Skype Online
Skype Online